What Is Child Neglect?
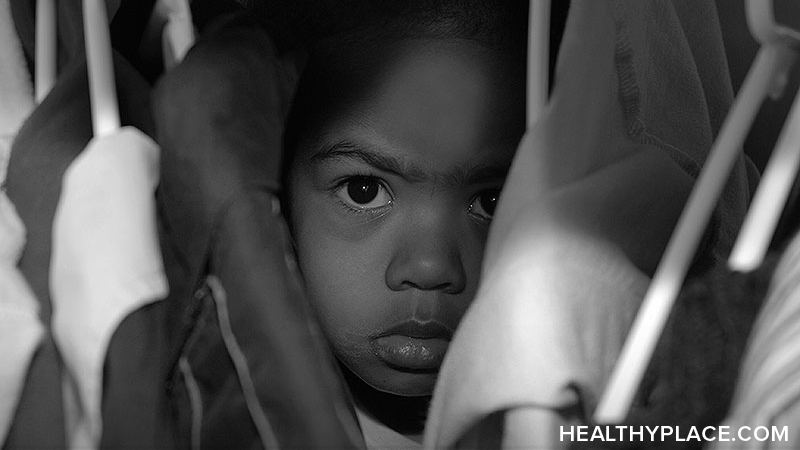
Child neglect is a serious problem in the United States. Over 550,000 child neglect victims were identified by Child Protective Services in fiscal year 2010. Child neglect can harm a child's self-esteem and sense of trust, delay them developmentally and put them at risk for other forms of abuse.
Definition of Child Neglect
Child neglect is the failure of a parent, guardian or other caretaker to sufficiently provide for the care of the child's basic needs. Child neglect may be:
- Physical – such as not providing food, shelter or supervision
- Medical – such as not providing medical or mental health treatment
- Educational – such as a failure to educate the child or attend to special needs
- Emotional – such as failure to provide psychological care or permitting the child to use alcohol or other drugs
Child neglect is a complex issue, as different cultures have different standards by which they view child neglect. For example, a religious belief may prevent a parent from obtaining medical care for their child. Poverty is also a major concern in child neglect and it may be the case that an above situation can occur due to poverty rather than child neglect.
Child neglect and abuse are often defined together in the law, but essentially, child abuse occurs due to harmful actions while child neglect occurs due to inactions.
Child Neglect Statistics
Of the approximately 1500 children that will die each year from child abuse and neglect, 30% of them will die due to child neglect alone1. Of the children who are abused or neglected, over 78% of them will experience neglect.
Child Neglect Laws
Child neglect laws are defined alongside child abuse laws at the federal and state level. Federally the child neglect laws are defined by The Federal Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act (CAPTA), (42 U.S.C.A. §5106g), as amended by the Keeping Children and Families Safe Act of 2003. At a minimum, child abuse and neglect is defined as 2:
- "Any recent act or failure to act on the part of a parent or caretaker which results in death, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse or exploitation
- An act or failure to act which presents an imminent risk of serious harm"
These laws refer to parents or caregivers and not to strangers or acquaintances. States build upon this definition and further specify child neglect and abuse laws. In general, child neglect refers to a failure to act whereas child abuse refers to an inappropriate (abusive) action; however, in many cases, neglect is simply considered a type of abuse.
Abandonment is also considered a form of child neglect in many states.
"In general, a child is considered to be abandoned when the parent's identity or whereabouts are unknown, the child has been left alone in circumstances where the child suffers serious harm, or the parent has failed to maintain contact with the child or provide reasonable support for a specified period of time.
Child neglect cases frequently center around physical child neglect, as emotional neglect can be hard to prove.
APA Reference
Tracy, N.
(2021, December 17). What Is Child Neglect?, HealthyPlace. Retrieved
on 2024, April 26 from https://www.healthyplace.com/abuse/child-abuse-information/what-is-child-neglect



